Publications
My reasearch is at the intersection of multimodal learning, large language models, and biomedical AI.
I build interpretable multimodal mixture-of-experts (MoE) systems, evaluate large language models, and apply machine learning to drug discovery and healthcare.
Quick Navigation
- Multimodal Representation & MoE
- Large Language Models Evals & Reasoning
- Biomedical AI & Computational Biology
Multimodal Representation & MoE
* denotes equal contribution
| Thumbnail | Details |
|---|---|
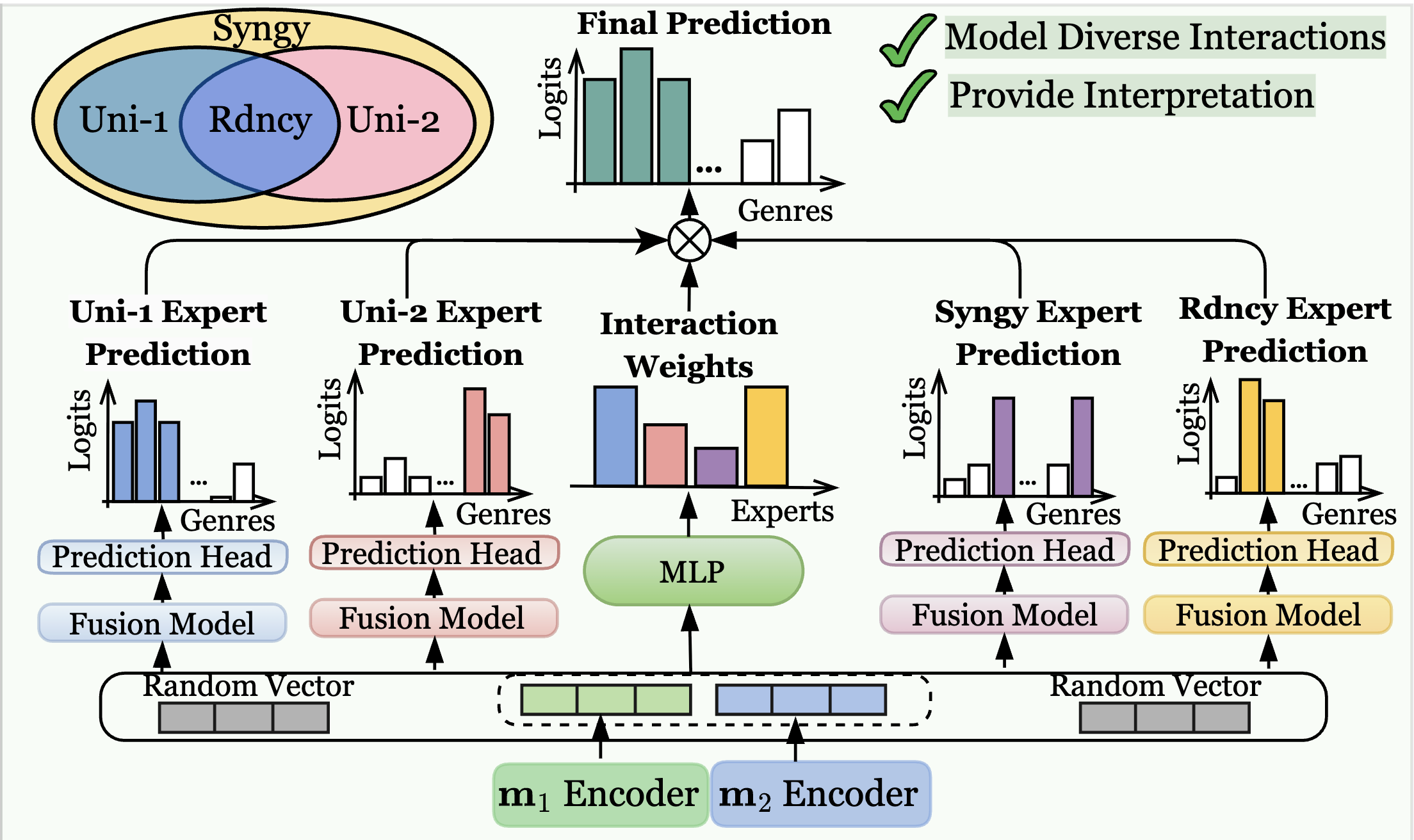 | I2MoE: Interpretable Multimodal Interaction-Aware Mixture-of-Experts Xin, J., Yun, S., Peng, J., Choi, I., Ballard, J. L., Chen, T., Long, Q. ICML 2025 We introduce a drop-in MoE framework that disentangles redundancy, synergy, and uniqueness interactions between different modalities, achieving superior multimodal fusion performance while exposing interaction weights for user interpretation. Paper |
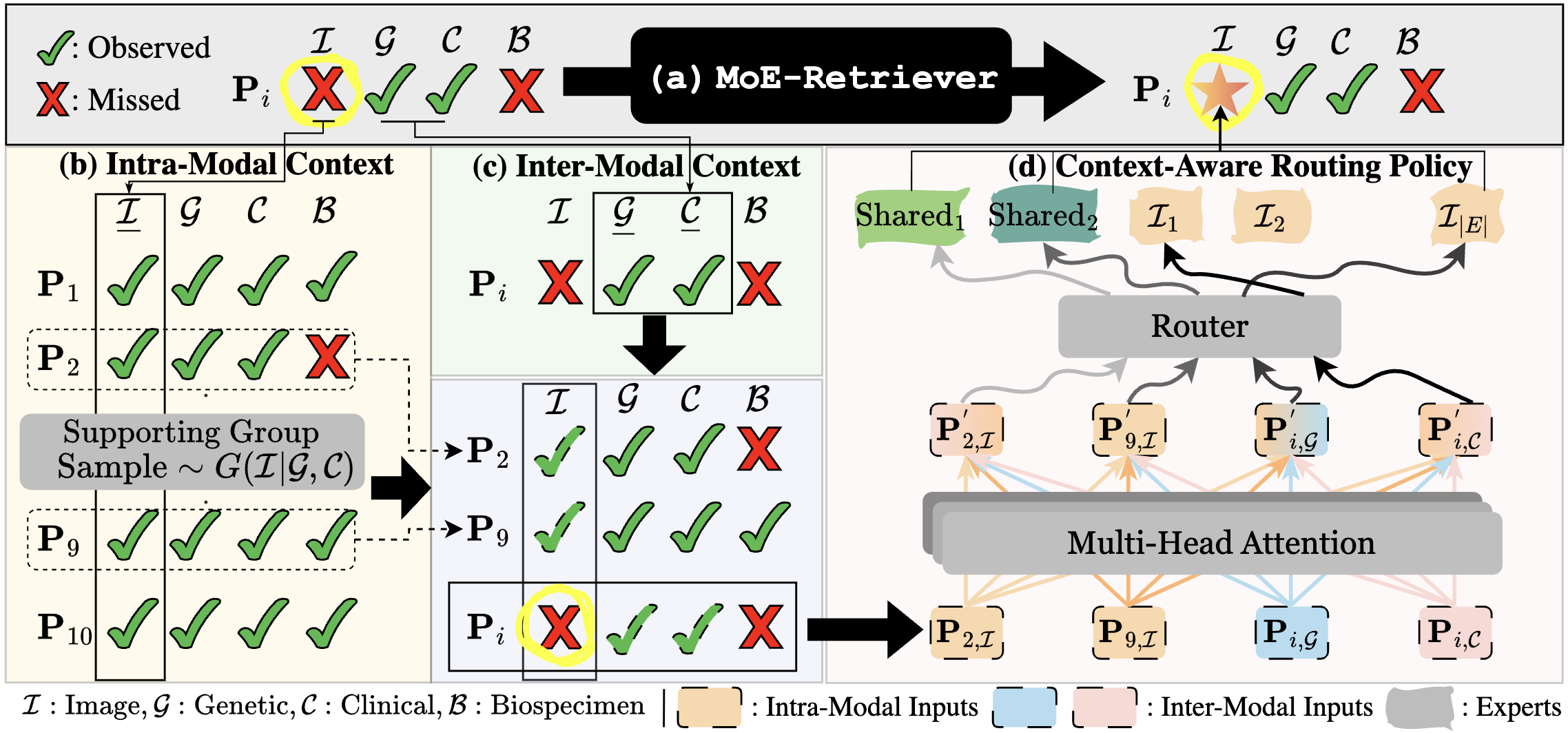 | Generate, Then Retrieve: Addressing Missing Modalities in Multimodal Learning via Generative AI and MoE Yun, S.*, Xin, J.*, Choi, I., Peng, J., Ding, Y., Long, Q., Chen, T. AAAI GenAI4Health Workshop 2025 Best Paper We impute missing modalities with learnable embeddings and route them through a sparse MoE, outperforming strong baselines on real-world multimodal datasets. Paper |
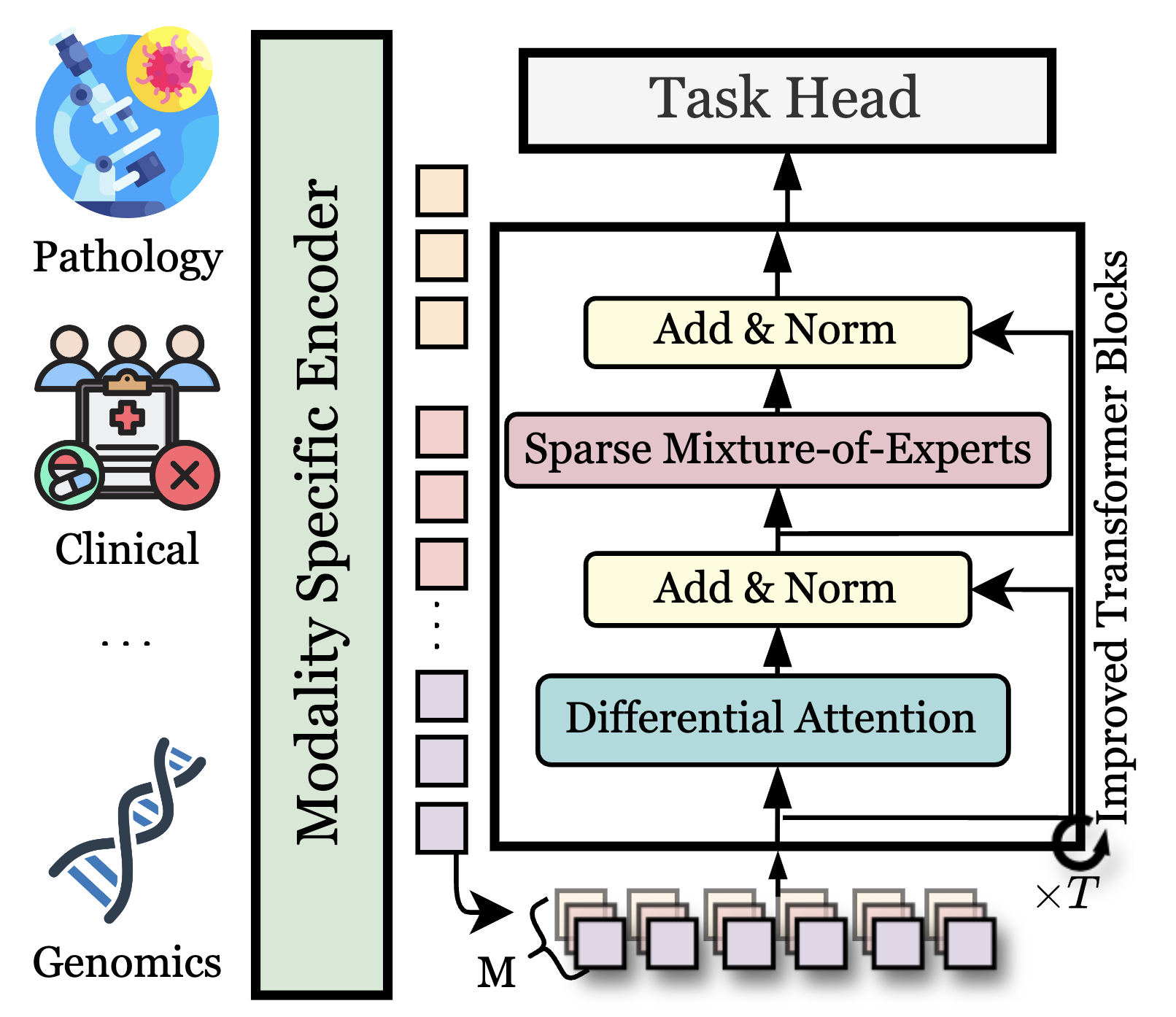 | Modalities Contribute Unequally: Enhancing Medical Multi-modal Learning through Adaptive Modality Token Re-balancing Peng, J.*, Ballard, J. L*,., Zhang, M., Yun, S., Xin, J., Long, Q., Zhang, Y., Chen, T. ICML 2025 We propose Adaptive Modality Token Re-BalanCing (AMC), a novel top-down dynamic multi-modal fusion approach. Paper |
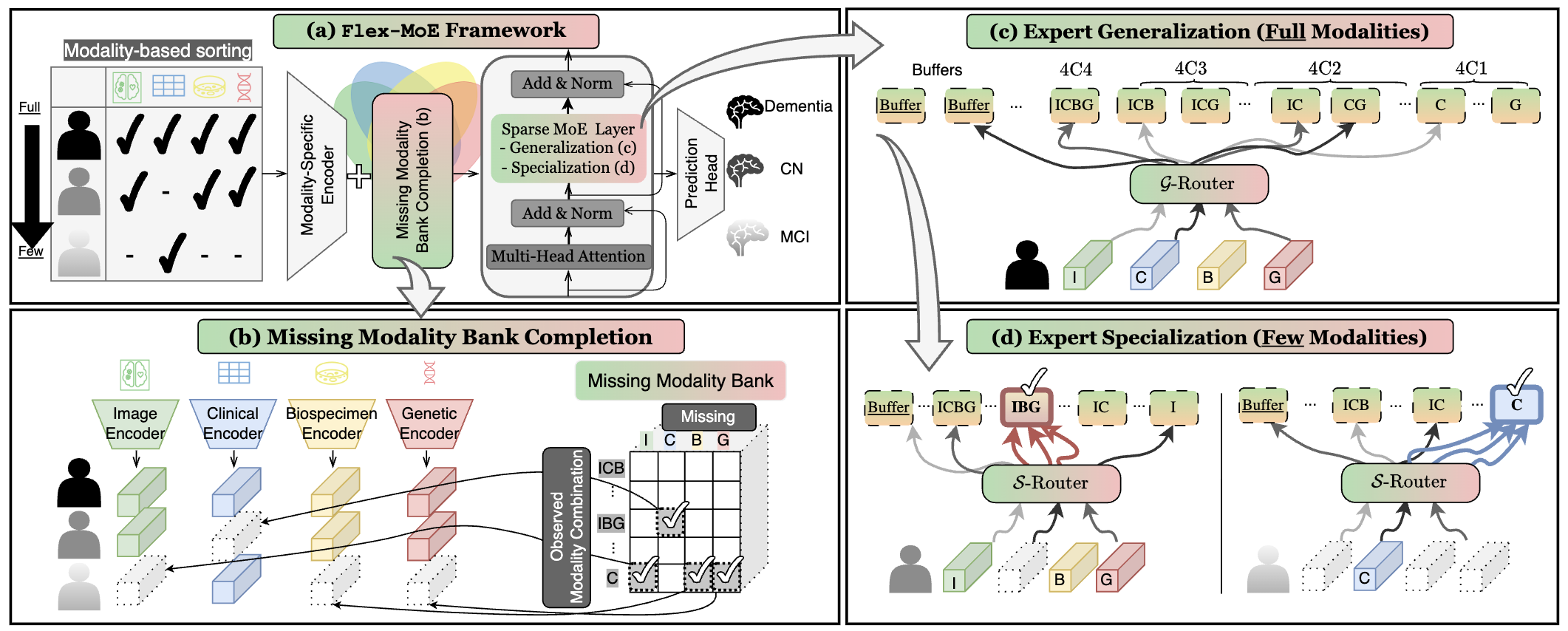 | Flex-MoE: Modeling Arbitrary Modality Combinations via the Flexible Mixture-of-Experts Yun, S., Choi, I., Peng, J., Wu, Y., Bao, J., Zhang, Q., Xin, J., Long, Q., Chen, T. NeurIPS 2024 Spotlight We propose Flex-MoE, new MoE framework designed to flexibly incorporate arbitrary modality combinations while maintaining robustness to missing data. Paper |
Large Language Models Evals & Reasoning
| Thumbnail | Details |
|---|---|
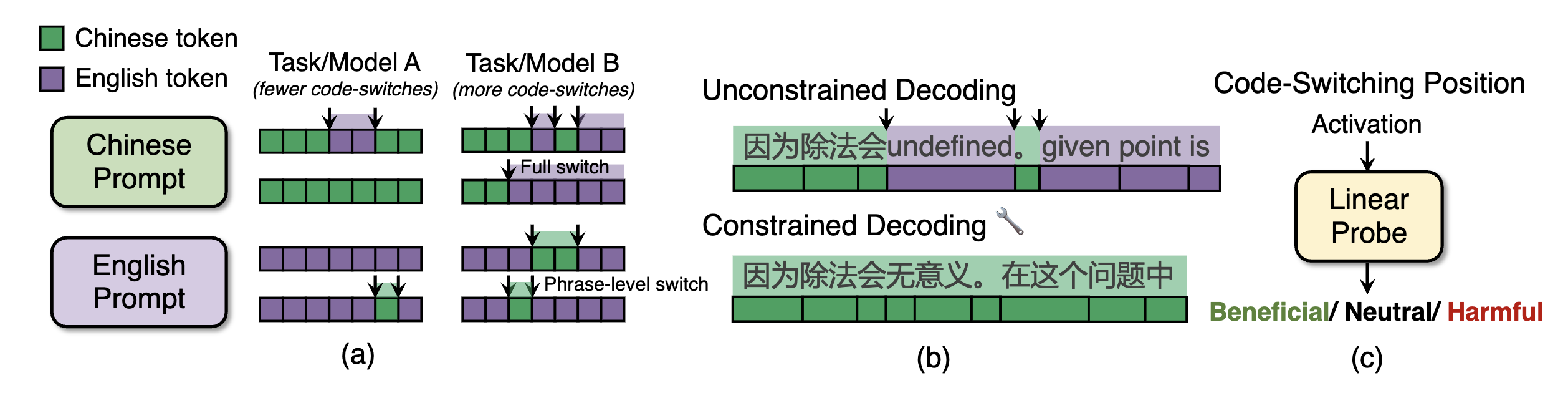 | The Impact of Language Mixing on Bilingual LLM Reasoning Li, Y., Xin, J., Miao, M. M., Long, Q., Ungar, L. EMNLP 2025 Oral We study language switching in Chinese-English bilingual reasoning models and trained a lightweight probe to predict whether a potential language switch would benefit or harm reasoning, and when used to guide decoding, increases accuracy by up to 6.25 pp. Paper |
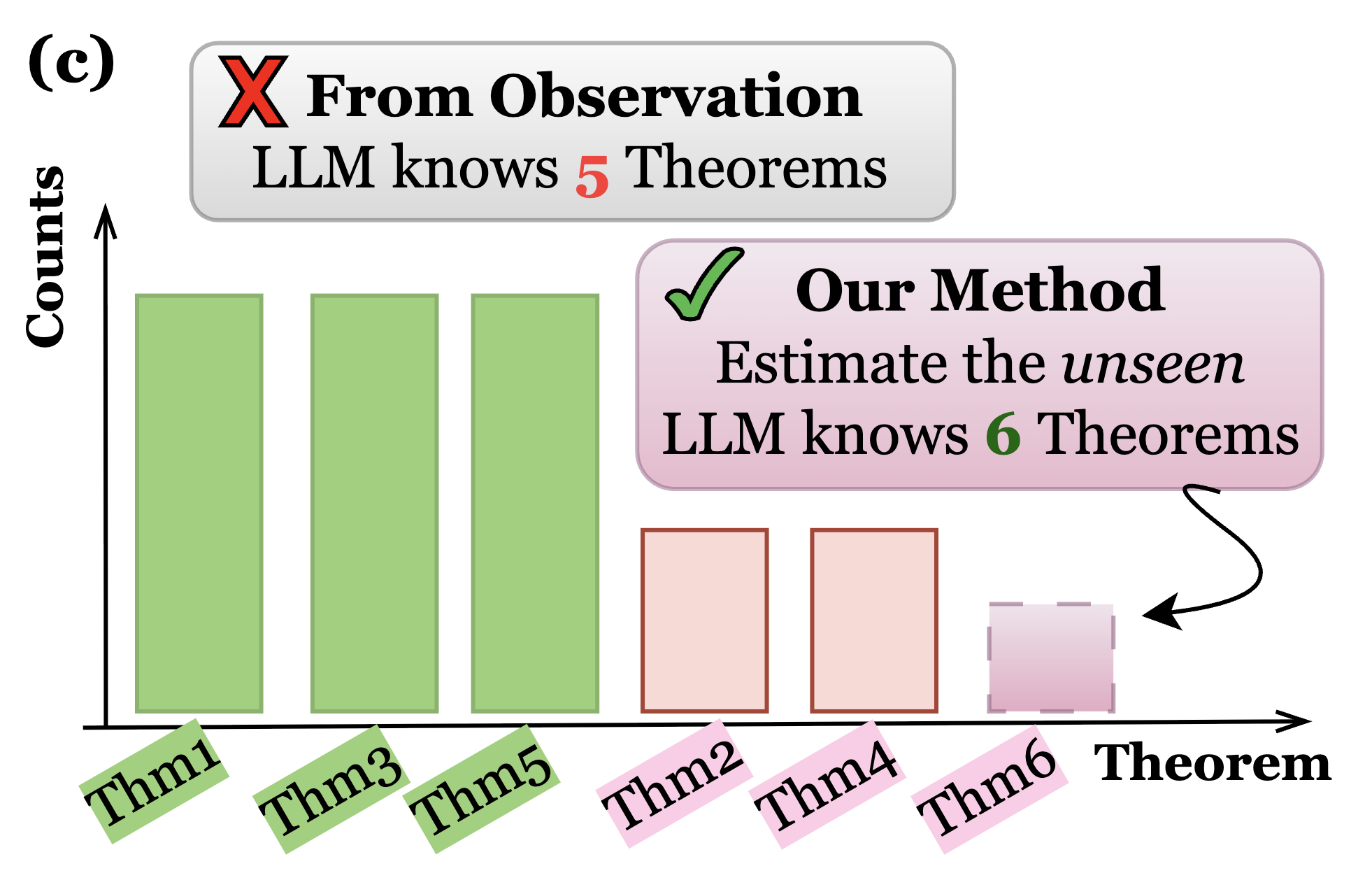 | Evaluating the Unseen Capabilities: How Many Theorems Do LLMs Know? Li, X., Xin, J., Long, Q., Su, W. Under review 2025 We introduce KnowSum, a statistical framework designed to provide a more comprehensive assessment by quantifying the unseen knowledge for a class of evaluation tasks. Paper |
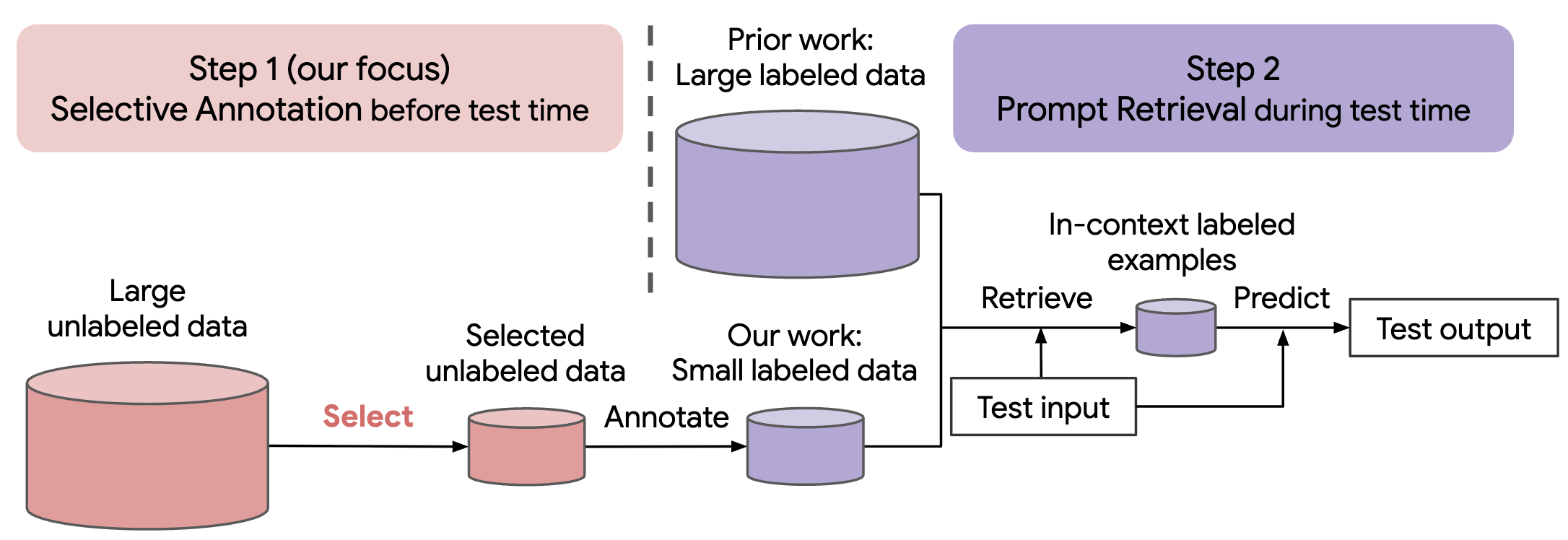 | Selective Annotation Makes Language Models Better Few-Shot Learners Su, H., Kasai, J., Wu, C.-H., Shi, W., Wang, T., Xin, J., Zhang, R., Ostendorf, M., Zettlemoyer, L., Smith, N. A., Yu, T. ICLR 2023 We formulate an annotation-efficient, two-step framework: selective annotation that chooses a pool of examples to annotate fromunlabeled data in advance, followed by prompt retrieval that retrieves task examples from the annotated pool at test time. Paper |
| Upcoming in 2026 January | One Paper about LLM Uncertainty Quantification |
Biomedical AI & Computational Biology
| Thumbnail | Details |
|---|---|
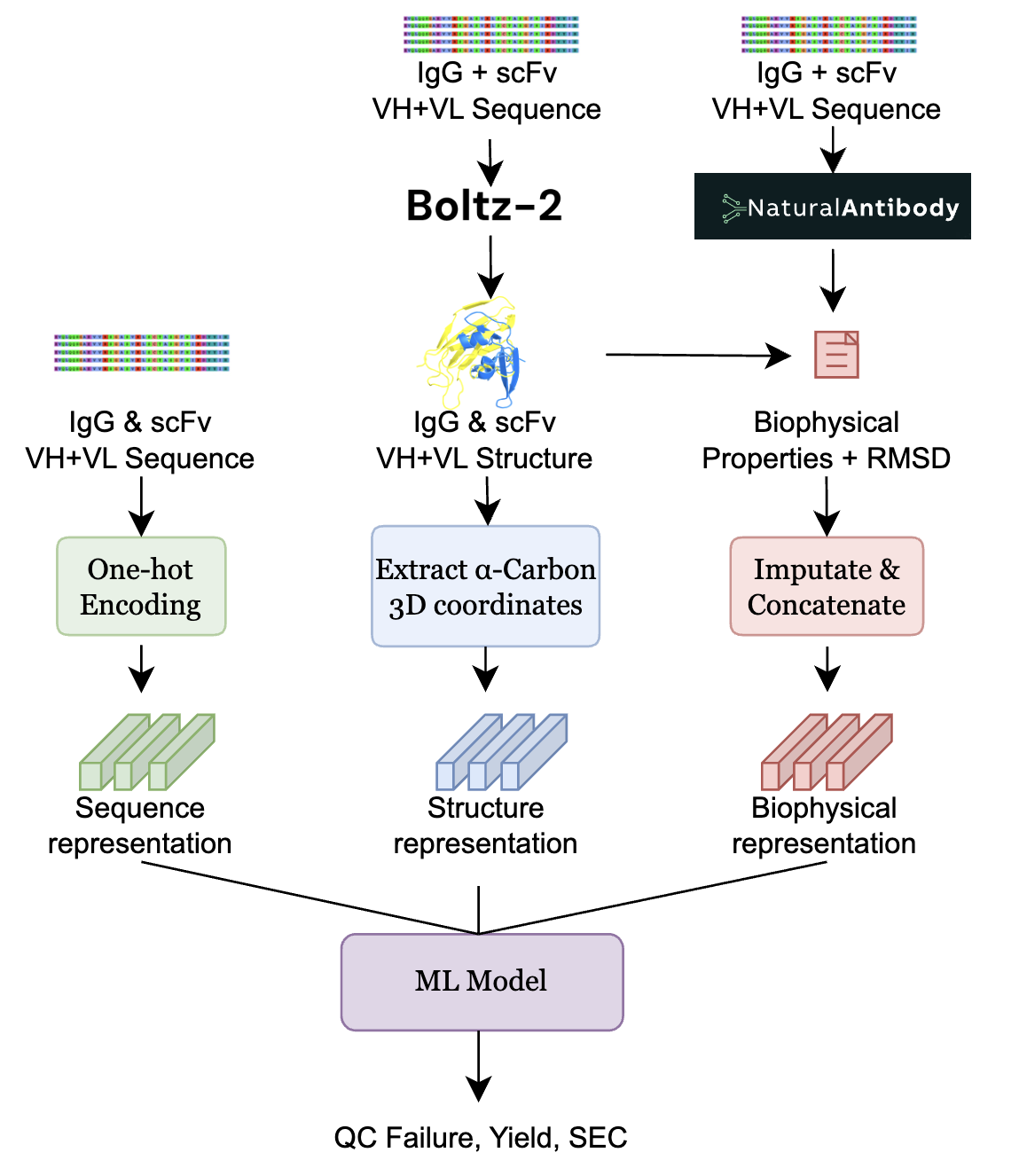 | Improved Therapeutic Antibody Reformatting through Multimodal Machine Learning Xin, J., Raghu, A., Bhattacharya, N., Carr, A., Montgomery, M., Elliott, H. NeurIPS 2025 AI4Science and FM4LS Workshop We develop a multimodal machine learning framework to predict antibody reformatting success, which incorporates both antibody sequence and structural context, and outperforms protein language models in an evaluation protocol that reflects realistic deployment scenarios. Paper |
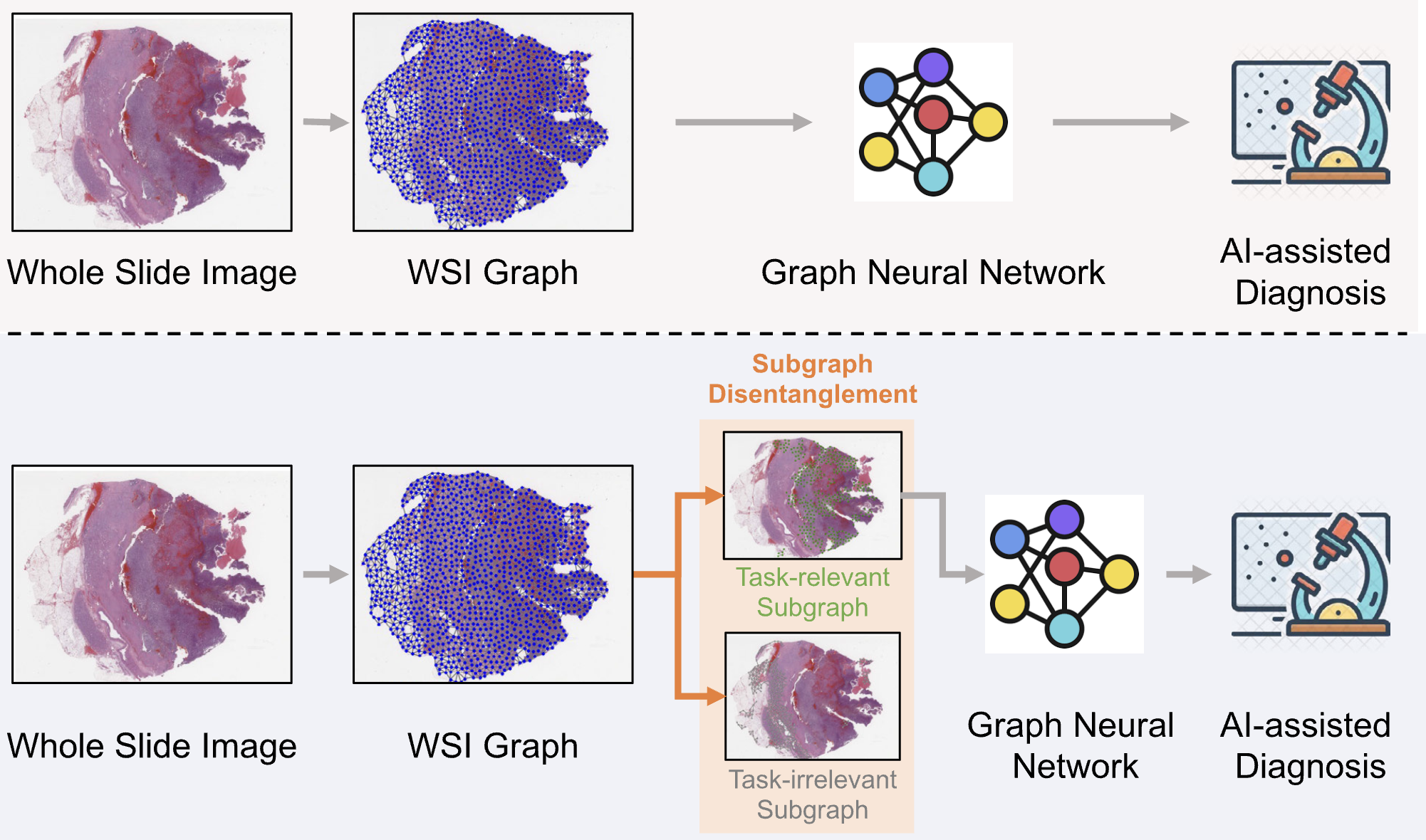 | TAD-Graph: Enhancing Whole-Slide Image Analysis via Task-Aware Subgraph Disentanglement Wang, F., Xin, J., Zhao, W., Jiang, Y., Yeung, M., Wang, L., Yu, L. IEEE TMI 2025 We propose a novel Task-Aware Disentanglement Graph approach that operates on WSI graph representations, effectively identifying and disentangling informative subgraphs to enhance contextual feature extraction. Paper |
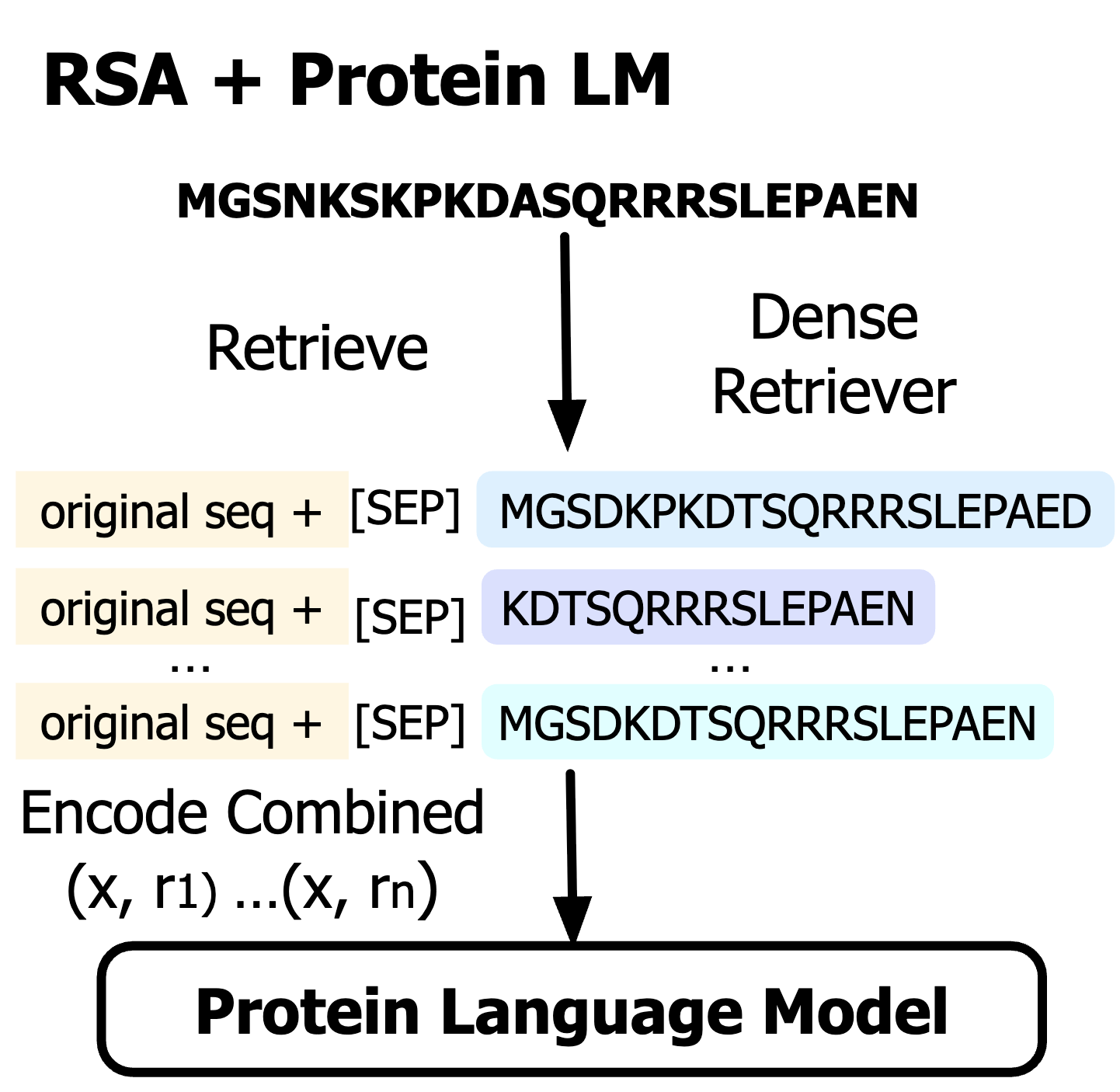 | Retrieved Sequence Augmentation for Protein Representation Learning Ma, C., Zhao, H., Zheng, L., Xin, J., Li, Q., Wu, L., Deng, Z., Lu, Y. Y., Liu, Q., Wang, S., Kong, L. EMNLP 2024 We show that a simple alternative, Retrieved Sequence Augmentation (RSA), can enhance protein representation learning without the need for alignment and cumbersome preprocessing. Paper |
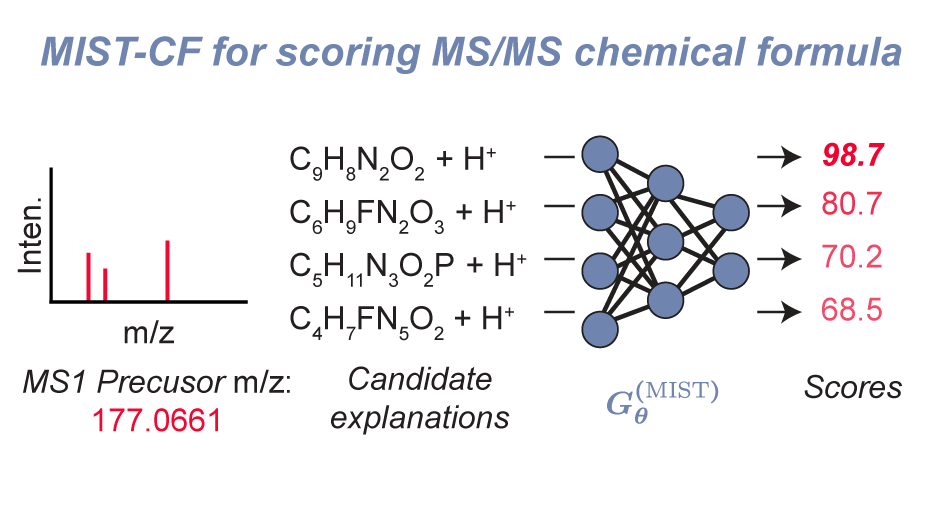 | MIST-CF: Chemical Formula Inference from Tandem Mass Spectra Goldman, S.*, Xin, J.*, Provenzano, J., Coley, C. W. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2023 We extend previous spectrum Transformer methodology for learning to rank chemical formula and adduct assignments given an unannotated tandem MS spectrum. Paper |
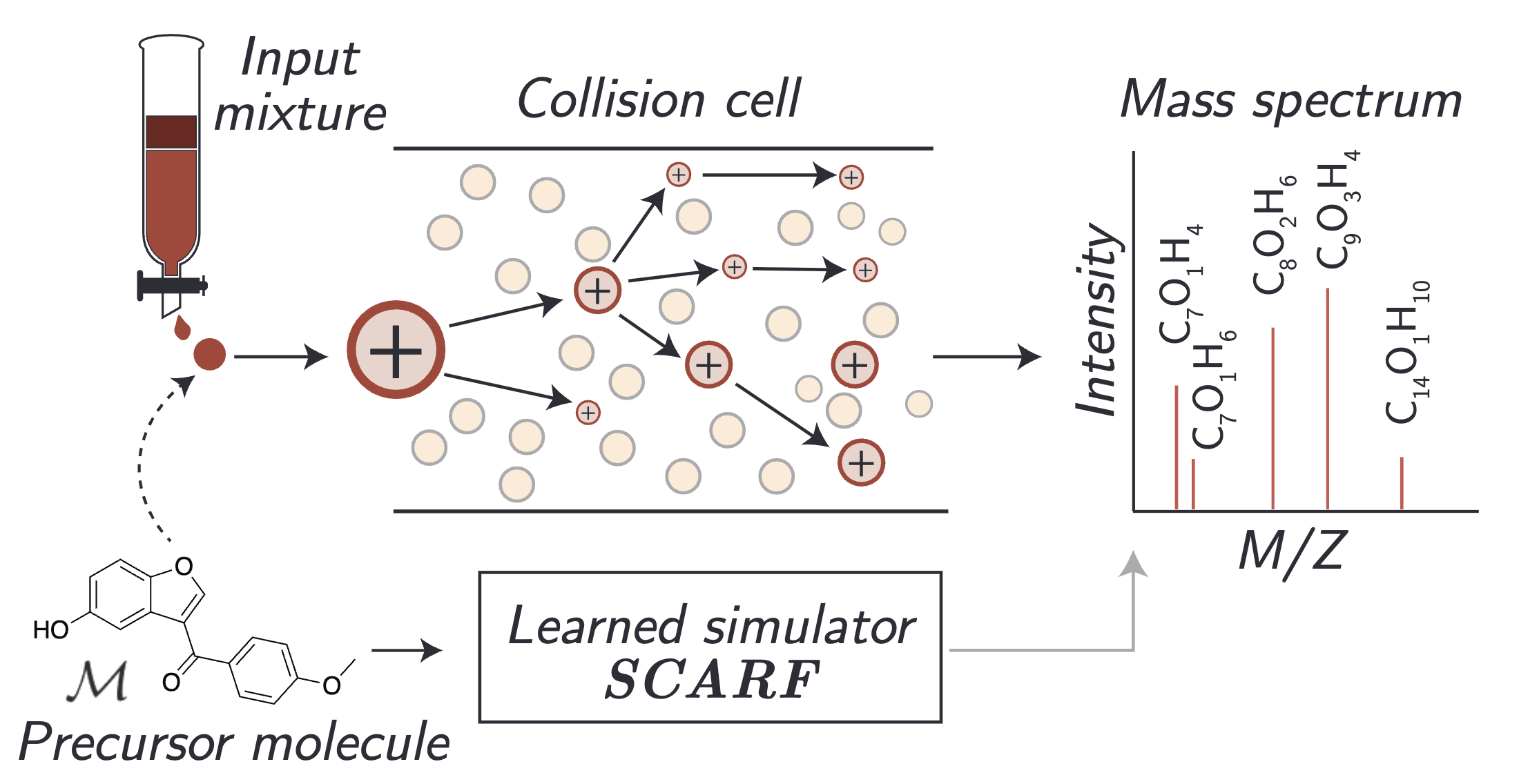 | Prefix-Tree Decoding for Predicting Mass Spectra from Molecules Goldman, S., Bradshaw, J., Xin, J., Coley, C. W. NeurIPS 2023 Spotlight We use a new intermediate strategy for predicting mass spectra from molecules by treating mass spectra as sets of molecular formulae, which are themselves multisets of atoms. Paper |
 | Artificial intelligence clinical applications of wearable technologies Ma, S., Yee, C. Y., Xin, J., Ho, J. W. K. Book chapter in Machine Learning, Medical AI and Robotics (IOP) 2023 We survey deep learning-based AI applications of wearable devices. Book Chapter |
